Guides & Tutorials
A Step-by-Step Guide: Phenomic on Netlify
Today, we’re going to look at how to host a website built with Phenomic on Netlify, including setting up continuous deployment.
Phenomic is a new static site generator built with ReactJS. React is a hugely popular JavaScript framework created in-house at Facebook.
Let’s start from scratch (if you already have a Phenomic site set up, you can skip down to here).
Prerequisites
Before you get started, know that Phenomic uses requires at least npm v3. If you have a different version of npm (which is installed along with node), we suggest installing nvm (the Node Version Manager) to allow you to change versions of node depending on the project. Different versions of node come with different versions of npm. Make sure your version of node is greater than 4.2.0, and your version of npm is greater than 3.0.0.
Learn about installing nvm in the nvm documentation.
Install Phenomic
Open your terminal, and enter the following command
$ nvm install 5.*
This will install the latest version of node (at the time of this writing, it's version 5.10.0). Next, specify that you want to use this version with this command
$ nvm use VERSION_NUMBER
With that out of the way, you can get started with Phenomic.
First, create a directory for your new sites.
$ mkdir PATH/TO/phenomic-site
Then change to that directory.
$ cd PATH/TO/phenomic-site
Now you can install Phenomic.
$ npm install phenomic
In your terminal, you may see a few error messages that look something like this:
npm WARN phenomic@0.11.0 requires a peer of redux@^3.0.0 but none was installed.
Go ahead and ignore them for now, they'll be taken care of in the next two steps.
Now that Phenomic is installed, you can set it up with this:
$ ./node_modules/.bin/phenomic setup
Phenomic will ask you a few questions. Answer them as you see fit, and say no to the CNAME file. You can set that with your DNS provider once you've got your site up and running and want to connect a custom domain.
Next, install the dependencies
$ npm install
This will install the dependencies listed in the package.json file you set up earlier.
Now it's time to take a look
npm start
Phenomic will launch a new window at localhost:3000 so you can see your handiwork.
Like what you see? Great. Let’s move on!
Prepping for Build
Netlify can use any number of versions of tools to build your site. But we need to tell Netlify which versions to use. Since Phenomic uses Node.js and NPM, we need to see which version you are running on your production machine. In the terminal enter the following:
$ node -v
The version (if you followed the nvm directions above) should be 5.10.0
Now check to see if Netlify supports your version of Node: https://github.com/netlify/build-image/blob/master/Dockerfile#L93. Look for a version close to yours (look for code along the lines of nvm install v5.1.0 if your version is 5.1.x).
To create a file to tell Netlify which version of Node.js to use, enter the following command in the terminal:
$ echo your.version.number > .nvmrc
On the computer used to create this tutorial, the node version is v5.10.0, so version 5.5.0 works. Therefore, the command used was echo 5.* > .nvmrc. Your version number may be different.
Now it’s time to push it to your repo of choice. Directions for GitHub follow here.
Creating your Git Repo
Create a new repository on GitHub. To avoid errors, do not initialize the new repository with README, license, or gitignore files. You can add these files after your project has been pushed to GitHub.
Open Terminal (for Mac users) or the command prompt (for Windows and Linux users).
For our purposes, let’s call your new repo phenomic.
Change the current working directory to your local project.
$ cd ~/PATH/TO/phenomic-site/
Initialize the local directory as a Git repository.
$ git init
Add the files in your new local repository. This stages them for the first commit.
$ git add .
Commit the files that you've staged in your local repository.
$ git commit -m 'First commit'
At the top of your GitHub repository’s Quick Setup page, click the clipboard icon to copy the remote repository URL.
In Terminal, add the URL for the remote repository where your local repository will be pushed.
git remote add origin Git_Repository_URL
Verify your URL
git remote -v
Now, it’s time to push the changes in your local repository to GitHub.
git push -u origin master
Now that your assets are up and running on GitHub, let’s connect them to Netlify.
Connecting to Netlify
Step 1: Add Your New Site
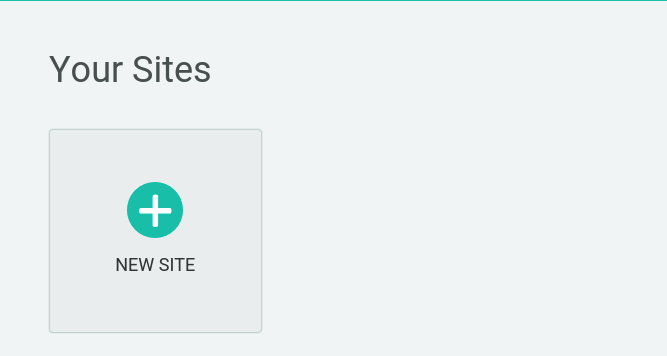
Creating a new site on Netlify is simple. Once you’ve logged in, you'll be taken to https://app.netlify.com/sites. If you’re just starting out, there’s only one option.
Step 2: Link to Your GitHub
Clicking “New Site” brings you to this screen:
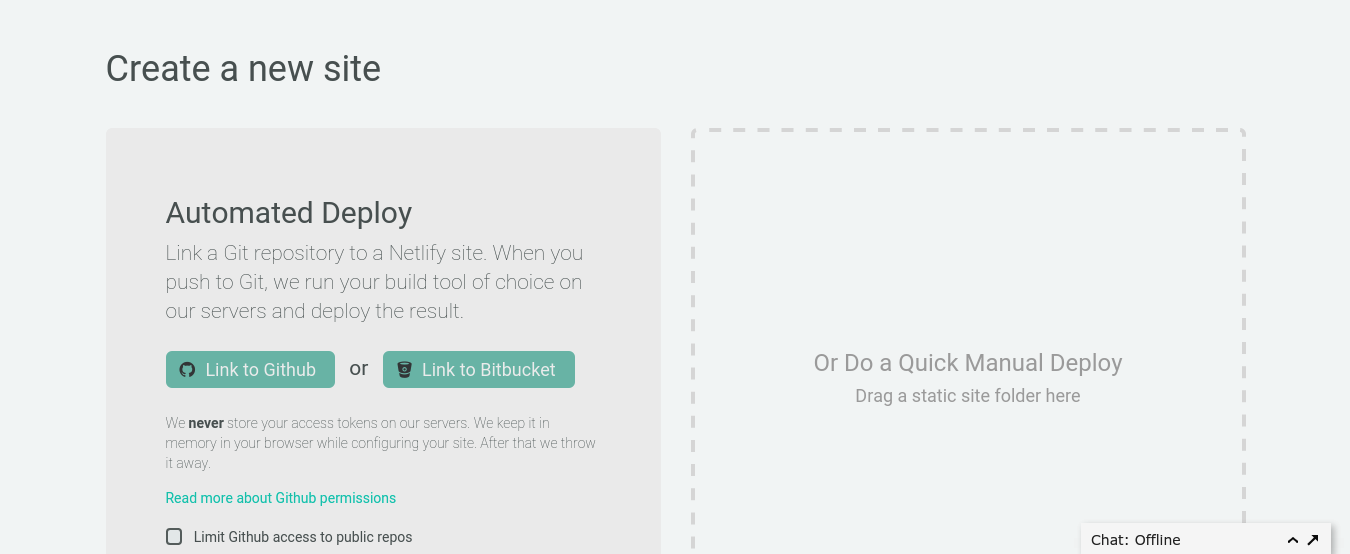
When you push to GitHub, Netlify does all the work. No more manual deploying of updates or changes!
Since your assets are hosted on GitHub, we’ll need to link Netlify to GitHub. Click “Link to GitHub”.
Step 3: Authorize Netlify
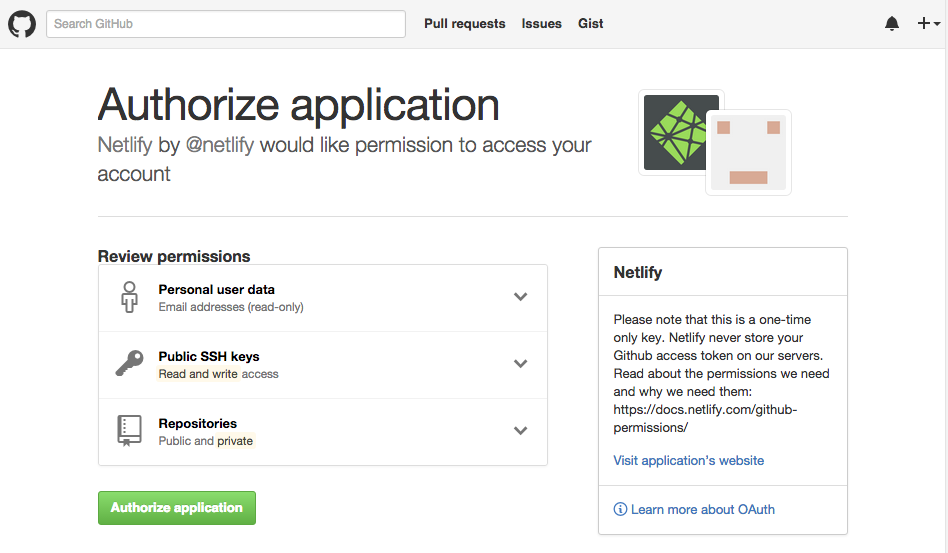
It’s time to allow Netlify and GitHub to talk to each other. Clicking the “Authorize Application” button will do just that. Like it says in the image below, Netlify doesn’t store your GitHub access token on our servers. If you’d like to know more about the permissions Netlify requests and why we need them, you can visit our documentation on Git provider permissions.
Step 4: Choose Your Repo
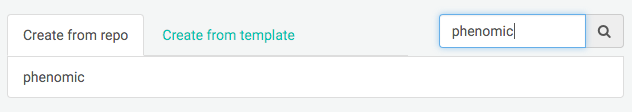
Now that you’ve connected Netlify and GitHub, you can see a list of your Git repos. There’s the phenomic repo we just pushed to GitHub. Let's select it.
Step 5: Configure Your Settings
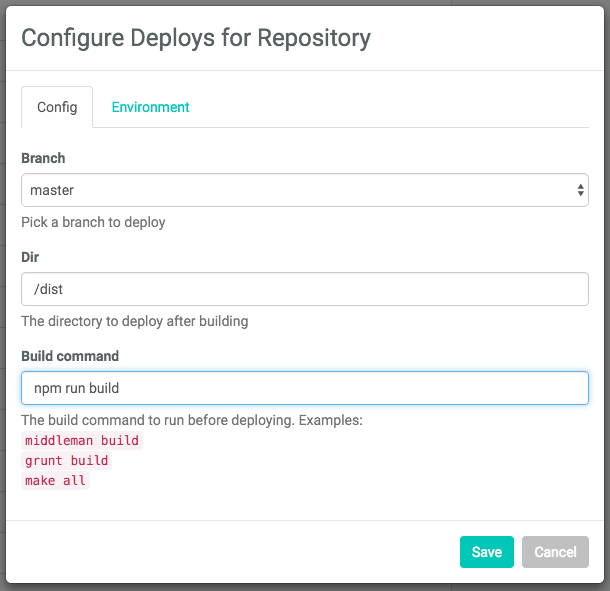
Here you can configure your options. Make sure that /dist is the directory you want to deploy, and enter npm run build as your build command.
Step 6: Build Your Site
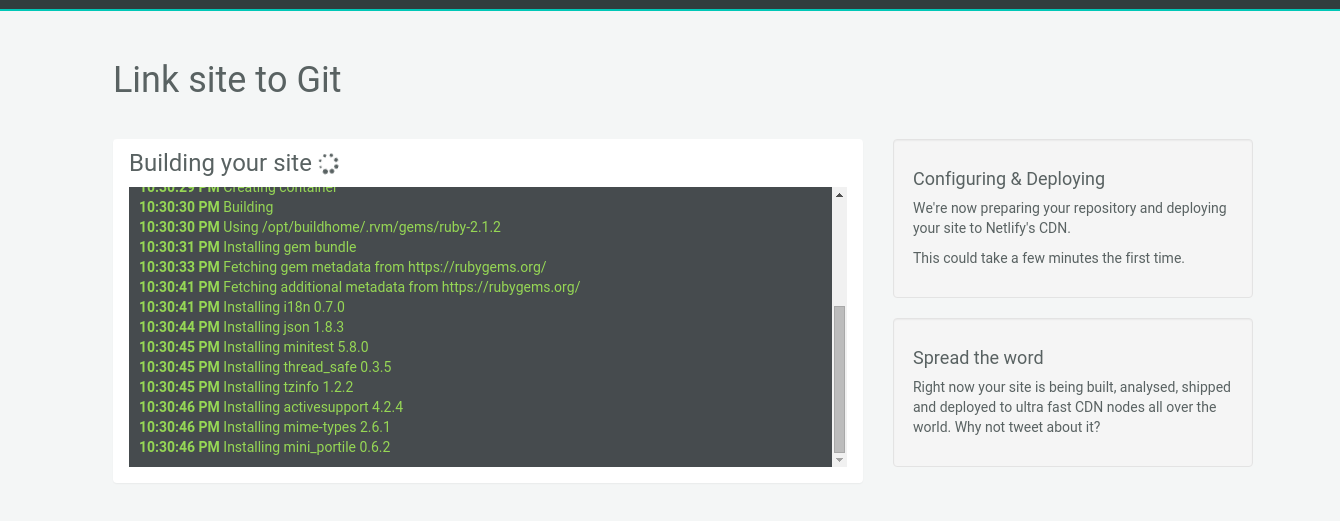
Now it’s time to sit back and relax. The first build will take some time, as Netlify gathers all the dependencies needed to build your site.
Step 7: Done
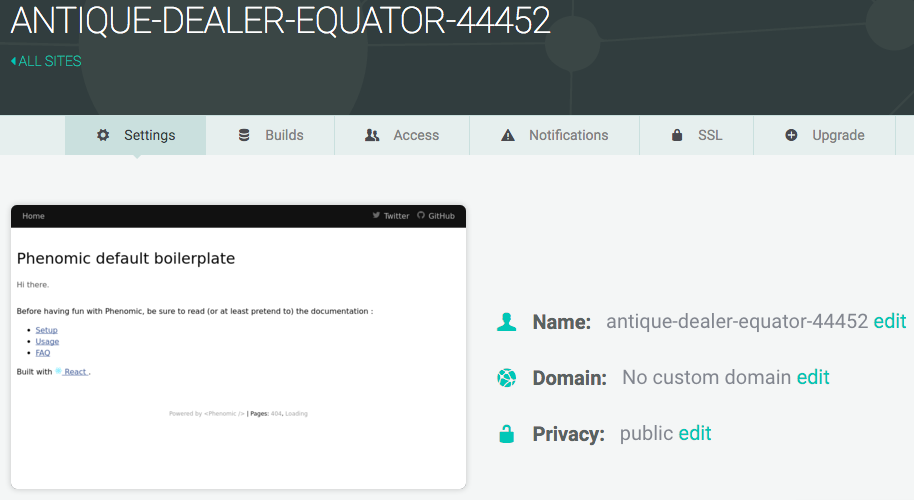
And...you're done! Netlify has done it all for you, including giving your site a temporary name. Now you can add your custom domain, and your site will be live for your adoring public to view. Congratulations, and thanks for using Netlify!


